Redundancy mechanisms turn a reliable system into a highly available system, adding extra components or functionality to maintain reliable operation through a number of failures. PROFINET allows you to build a reliable network according to your specific requirements. Specifically, PROFINET offers four redundancy options: Device Redundancy, Controller Redundancy, Network Redundancy, and Media Redundancy.
Device Redundancy
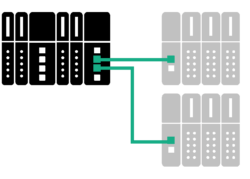
A network with device redundancy has a singular controller connected to multiple devices, as shown below. The controller establishes a connection to both devices simultaneously and sends the same output data to both devices. However, it marks the data sent to the secondary device as “invalid” while the data sent to the primary as “valid.” When a failover is triggered, the controller marks the secondary output data as “valid.” Then, the secondary device can take over from the primary one seamlessly and without delay. Device Redundancy can work with any PROFINET device; however, controllers must support it.
Controller Redundancy
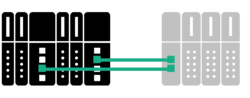
A network with controller redundancy has more than one controller connected to a device simultaneously, as shown below. In the presence of two controllers, the first one establishes a primary connection, and the second controller establishes a “backup” connection. The backup link doesn’t contain any valid output data. The secondary controller cannot change any options on the device.
Eventually, if the primary controller fails, the device waits for the backup controller to request a transition to primary status. Then, the new primary controller coordinates the change across the entire PROFINET network. Controller Redundancy requires support from both the device and the controllers.
Network Redundancy
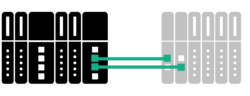
Network redundancy allows a network to continue running after a subnet failure by swapping communication to a second subnet. With network redundancy, a device employs two interface modules to communicate over two separate PROFINET networks, as shown below. Each network module has an independent Application Relation [1] (AR) with the PROFINET controller (2 subnets). Network redundancy requires support from both the device and the controller. Also, the device must have two interface modules.
Media Redundancy
Ring topologies establish media redundancy. If a wire breaks in one section of the ring, there is a secondary connection to the network. You can set up ring topologies and establish media redundancy in PROFINET networks. For more information, read our complete post on PROFINET Media Redundancy.
[1] Application Relation: The relationship between a PROFINET Controller and a PROFINET Device. A PROFINET device can support more than one Application Relationship.
For more information, read the full white paper below:
-Nelly Ayllon