The terms Ethernet and Industrial Ethernet often create confusion as they are often used interchangeably. This post makes a comparison between Ethernet and Industrial Ethernet.
Ethernet and Industrial Ethernet are the same thing. The only difference is that Industrial Ethernet includes running Ethernet traffic over more ruggedized hardware. For example, the cabling employed for Ethernet-based communications can vary substantially across applications.
Ethernet cables can be classified according to their network characteristics (i.e., Cat 5, Cat6, Cat7). On top of that, they can be classified as either commercial Ethernet (often referred to as just ‘Ethernet’) or Industrial Ethernet.
On the wire, Ethernet and Industrial Ethernet are identical. Their specifications (i.e., transmission speed and bandwidth) apply across different cable types. However, their target applications vary.
Commercial Ethernet hardware is not designed for usage in industrial applications. It is more suited for standard consumer environments, such as home and office networks. In those locations, cables are not exposed to extreme environmental conditions or excessive stress. On a factory floor, however, commercial Ethernet cables can damage and break easily. Employing commercial Ethernet hardware in industrial applications is extremely risky, as hardware failures can interrupt critical and expensive processes.
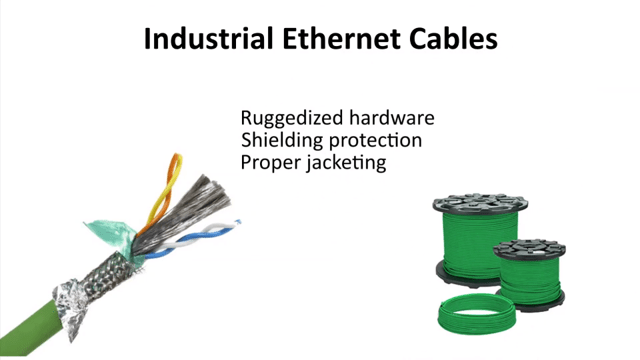
Industrial Ethernet cables and hardware are designed for industrial applications. Industrial environments are characterized by challenging conditions, such as extreme temperatures, humidity, vibrations, and electromagnetic interference. Industrial Ethernet hardware is rugged, and its wiring is protected with shielding and jacketing.
Learn more about Ethernet and industrial Ethernet by watching this free on-demand webinar.